Learn about liquidity ratios and their most important types and formulas

Liquidity ratios are among the most important accounting measures, as they assess a company’s financial health, stability, and ability to meet obligations on time. But what is the impact of liquidity ratios on investment decisions and the ability to grow and expand? How can a strong financial reputation in the market be achieved through liquidity ratios?
All these questions and more are answered in the lines of this article through a scientific and detailed explanation of the importance of the quick ratio, its types, and methods of calculation, in addition to clarifying how to read liquidity ratios in a way that helps manage assets effectively, prepare for crises, and improve financial performance and competitive position in labor markets.
What are liquidity ratios?
Liquidity ratios are financial measures that assess a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations and convert assets into cash quickly, without incurring significant losses or requiring external assistance.
The cash ratio provides valuable insights into a company’s liquidity position and its ability to repay debts, cover operating expenses, and pursue investment opportunities. It is commonly used by investors, creditors, and financial analysts to evaluate a company’s financial condition and asset management efficiency.
Liquidity ratios are considered one of the most important financial ratios necessary to evaluate a company’s short-term financial health. They are used alongside other financial measures to gain a comprehensive understanding of overall financial performance and company stability.
The level of cash coverage for daily cash needs varies by industry; therefore, comparisons should be made within the same industry or sector to obtain accurate and logical evaluations of liquidity ratios.
What are the types of liquidity ratios?
Calculating liquidity ratios is essential in financial analysis to assess a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations by converting assets into cash more quickly. There are several types of liquidity ratios, each with its own meaning and importance in financial analysis.
Below are the most important liquidity ratios for evaluating companies' financial health.
- Current ratio
- Quick ratio
- Cash ratio
- Net working capital
- Cash coverage ratio for daily cash needs
- Operating cash flow ratio
1- Current Ratio
The current ratio, also known as the current liquidity ratio, is the most common liquidity ratio and measures how well a company’s current assets can cover its current liabilities within one year.
Current assets are those that can be converted into cash within one year, such as marketable securities, money, and inventory.
Current liabilities, or short-term liabilities, include obligations due within one year, such as salaries, rent, and taxes.
Formula for calculating the current ratio:
Current ratio = Total current assets ÷ Total current liabilities
If total current assets are $18,000 and total current liabilities are $10,000, then the current ratio = 18,000 ÷ 10,000 = 1.8 (which means that current assets cover current liabilities by 1.8 times).
Daftra automatically calculates the current ratio after collecting the necessary data from current asset and current liability accounts, including cash, inventory, loans, and others, as the system is interconnected and integrated.
You can also download a ready-made template to calculate the current ratio quickly.
2- Quick Ratio
The quick ratio measures a company’s ability to cover current liabilities with current assets that can be liquidated quickly. Accordingly, current assets in this case do not include inventory, which is considered one of the least liquid and slowest assets to be liquidated, nor prepaid expenses, because they take a long time to be converted into cash.
Formula for the quick ratio:
Quick ratio = Total current assets − inventory − prepaid expenses ÷ total current liabilities
For example, if the total current assets of your company are $150,000, inventory is estimated at $10,000, and prepaid expenses are estimated at $5,000, while total current liabilities are $150,000.
The quick ratio equals 150,000 ÷ 10,000 − 5,000 − 150,000 = 0.9 (which means that the company can cover only 90% of its current liabilities).
You can download a quick ratio calculation template here to streamline the process.
3- Cash Ratio
The cash ratio measures a company’s ability to meet current obligations with cash on hand. Therefore, only marketable securities and cash on hand are considered from current assets.
Formula for the cash ratio:
Cash ratio = Cash + marketable securities ÷ total current liabilities
4- Net Working Capital
The net working capital ratio is the difference between current assets represented by short-term investments and accounts receivable, and current liabilities represented by supplier debts, shareholder obligations, long-term loans, and others.
5- Cash Coverage Ratio
The cash coverage ratio, used to assess the period during which a company can cover its daily cash needs, is one of the liquidity ratios.
6- Operating Cash Flow Ratio
The operating cash flow ratio measures a company’s ability to cover its debt service obligations with cash flows generated by operating activities.
Daftra calculates the operating cash flow ratio using the necessary data from the cash flow statement, then analyzes it. If the ratio is above 1, it indicates the company’s ability to meet its obligations; otherwise, it indicates financial risk.
Read also: Debt ratios and how to calculate them.
What is the importance of liquidity ratios?
Liquidity ratios help measure a company’s ability to convert its assets into cash quickly for day-to-day operations, such as purchasing inventory, paying employee salaries, and covering other expenses necessary to maintain operations and production. This is done through evaluating the cash ratio.
Liquidity ratios are also used to assess whether a company has sufficient liquid assets to maintain smooth operations and avoid financial crises. Below are the most critical factors that explain the importance of liquidity ratios:
1- Identifying financial risk
A low liquidity ratio reflects potential financial risks that weaken a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. Conversely, a high liquidity ratio indicates the company’s ability to meet debt obligations on time, with cash surplus available for investment and growth.
2- Providing a comprehensive picture of the financial position
Liquidity ratios provide integrated insights for decision-makers into a company’s financial position, helping them anticipate financial planning strategies to manage emergencies, address unexpected expenses, and avoid financial distress.
Here, it is essential to distinguish between financial distress and financial hardship. The former refers to the presence of revenues insufficient to meet short-term obligations, as measured by liquidity ratios. In contrast, financial hardship refers to the inability to generate any profit from the institution's revenues, as measured by profitability ratios.
3- Attracting investors and financiers
Companies with high liquidity ratios have higher credit ratings and creditworthiness, making them more attractive to investors and financiers. Capital owners tend to invest in companies that demonstrate strong liquidity management.
4- Improving managerial decision-making
Management uses liquidity ratios to evaluate the effectiveness of strategies for managing current assets, such as cash, marketable securities, inventory, and accounts receivable. This supports budget preparation, enables sound investment decisions, improves resource allocation through greater efficiency and effectiveness, and rationalizes costs and expenses.
5- Evaluating operational efficiency
Liquidity ratios are used to measure the extent to which an organization achieves its financial objectives through the efficiency of daily operational and production processes, including the payment of obligations, wages, and the purchase of goods.
6- Adapting to economic changes
High liquidity ratios help companies adapt to sudden economic changes, including inflation, rising interest rates on loans and financing for investment and expansion, and economic recession.
7- Managing cash flows efficiently
Liquidity ratios are used to maintain inbound cash flow at a level higher than outbound cash flow. High liquidity ratios help secure cash discounts when settling obligations to banks and creditors early, thereby improving cash flow.
How are liquidity ratios calculated?
Liquidity ratios in financial analysis are calculated using specific formulas for each type. Liquidity ratios vary across companies based on the portion of assets that can be liquidated and how readily they can be converted into cash.
Now, let us apply this in practice with a hypothetical company, “Al-Ru’a,” operating in the import and export sector, to see how we calculate the different liquidity ratios and interpret them.
Current assets: $600,000
Current liabilities: $300,000
Inventory: $100,000
Cash and cash equivalents: $200,000
We will now calculate the three main liquidity ratios: the current ratio, the quick ratio, and the cash ratio.
1- Current ratio
600,000 / 300,000 = 2
The current liquidity ratio (2) indicates that Al-Ru’a Company has $2 in current assets for every 1 riyal in current liabilities, which means the company can comfortably cover its short-term obligations.
2- Quick ratio
(600,000 − 100,000) / 300,000 = 1.5
The quick ratio (1.5) indicates that the company has $1.50 in quick assets (excluding inventory) for every 1 riyal of current liabilities. This ratio provides a more accurate measure of liquidity and indicates a reasonable ability to meet short-term obligations without relying heavily on inventory.
3- Cash ratio
200,000 / 300,000 = 0.67
The cash ratio (0.67) indicates that the company has $0.67 in cash for every 1 riyal of current liabilities. This ratio is relatively low; however, it still shows sufficient liquidity to meet immediate obligations with available cash.
Overall, based on liquidity ratios, Al-Ru’a Company appears to have a strong liquidity position, indicating its ability to meet its short-term obligations comfortably.
If you would like to calculate the cash ratio for your company, you can now download a cash ratio template from Daftra, ready for editing and free to use.
The Daftra accounting system can calculate liquidity ratios in seconds using previously entered data. Using an integrated accounting system also ensures obtaining accurate data.
What are the factors affecting liquidity ratios?
Liquidity ratios are influenced by several factors that must be well understood to inform strategic decisions that support a company’s ability to meet its financial obligations and improve its overall financial position. The most prominent factors affecting liquidity ratios include the following:
1- Nature of current assets
Liquidity ratios are affected by the type of current assets. Liquid current assets, such as cash and accounts receivable, improve liquidity ratios relative to non-liquid current assets, such as inventory.
2- Poor inventory management
- High inventory levels tie up capital. Excess inventory beyond what is necessary increases storage and maintenance costs, reducing liquidity available for other uses and negatively affecting cash flows.
- Damage to or decline in the value of excess or unsold inventory over time leads to additional cash losses, which negatively affect liquidity ratios.
- Supply and supply chain issues that affect inventory availability impair the company’s ability to meet customer requirements and, consequently, affect the liquidity ratios planned for a specific time period.
- Failure to use inventory and warehouse management software makes it difficult to accurately track inventory levels, exposing the company to risks of excess or shortages beyond required levels, which negatively affect liquidity ratios.
- Changes in customer preferences also lead to inventory accumulation and reduced liquidity.
The Daftra system includes an integrated inventory management program that is highly efficient, and you can customize it to suit your business needs.
3- Timing of obligations’ maturity
Liquidity ratios are affected by the due dates of current obligations as well as their size. If obligations are short-term debts, the company’s ability to repay them using available liquidity ratios increases. An increase in financial obligations also affects liquidity and makes it more difficult for the company to meet obligations that exceed the available level of liquidity.
4- Market fluctuations
Changes in market trends and increased competition affect sales, revenues, and profits, which in turn affect cash flows and liquidity ratios.
Liquidity ratio template
We provide a template that lets you calculate current, quick, and cash liquidity ratios for four consecutive years, enabling you to compare results and assess whether your asset management and liquidity ratio plans are yielding results.
Download the liquidity ratios template for free from here.
Who benefits from liquidity ratios?
Liquidity ratios are important to many parties involved in the business world, as they are a fundamental measure in evaluating a company’s financial position, its ability to repay debts, and improving financial performance. Below are the main beneficiaries of liquidity ratios:
1- Investors
Investors use liquidity ratios to assess companies’ ability to meet their financial obligations and to identify investment opportunities in companies with a strong financial position relative to competitors.
2- Financiers and suppliers
Banks and financial institutions rely on liquidity ratios to determine a company’s ability to repay loans. Good liquidity ratios enhance the chances of obtaining financing on favorable terms, such as lower interest rates or longer repayment periods.
3- Financial analysts
Financial analysts and auditors use liquidity ratios when preparing accounting reports to evaluate companies' financial health, enabling well-informed, evidence-based recommendations to investors and lenders.
How does Daftra help you improve liquidity ratios?
Daftra’s cloud-based accounting software helps improve liquidity ratios through the many smart and accurate solutions it provides. Once you activate your Daftra account, you can manage liquidity ratios as follows:
1- Preparing cash flow reports from operating, investing, and financing activities easily, and obtaining accurate results about available liquidity.
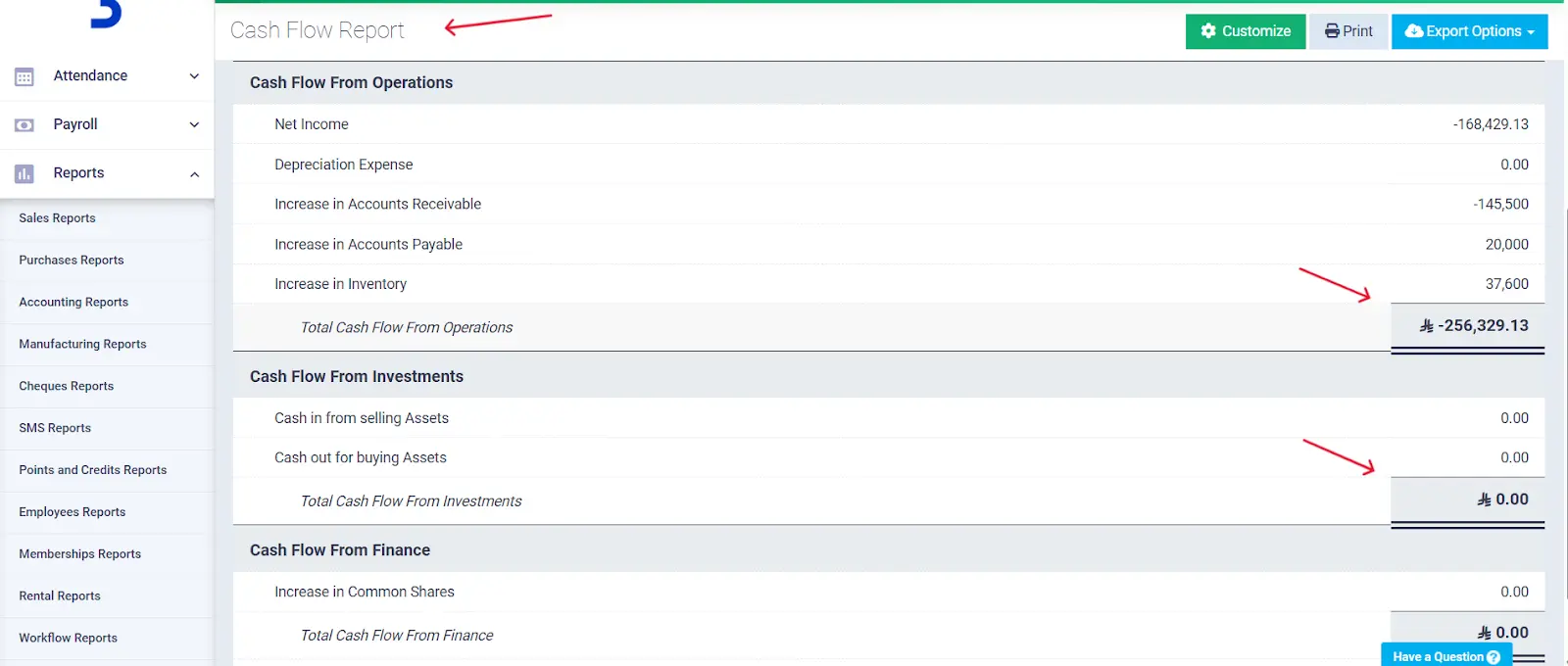
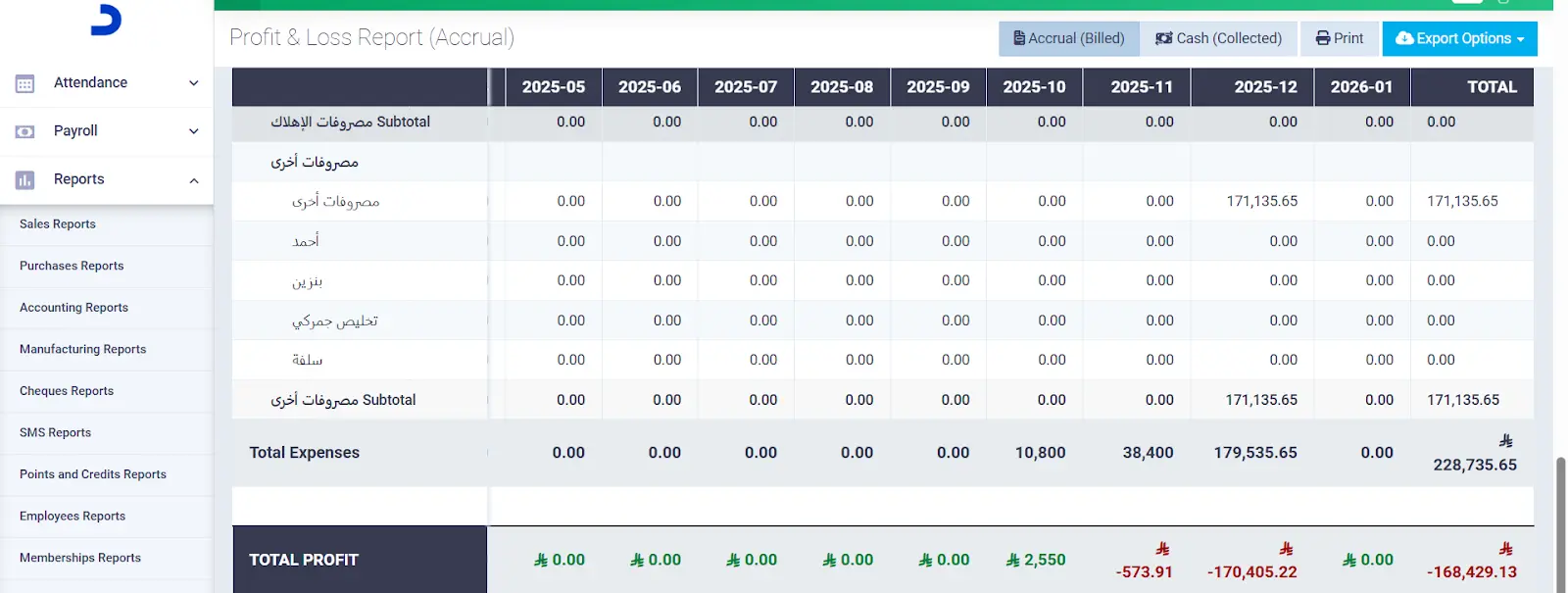
2- Managing expenses and revenues, and obtaining detailed profit reports, which contribute to controlling liquidity ratios and improving them.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the domestic liquidity ratio?
Domestic liquidity measures the level of liquidity within a country, represented by the central bank. It determines the total cash held by the central bank to support the country's ongoing financial operations and is often measured in an international currency, such as the US dollar.
What are the most common liquidity ratios?
The current ratio and the quick ratio are considered among the most common and widely used liquidity ratios, due to the clear and rapid insights they provide into a company’s financial position.
The current ratio compares current assets to current liabilities, reflecting the company’s ability to repay its short-term obligations. Therefore, it is an indicator of the company’s stability and its ability to meet immediate financial obligations. In addition, the current ratio reflects the efficiency with which the company manages its current assets.
On the other hand, the quick ratio reflects the institution’s ability to meet current liabilities with liquid assets, without resorting to inventory sales. Therefore, the quick ratio is an immediate indicator of the company’s financial position and helps manage and assess risks associated with changes in the inventory market.
How is liquidity identified in stocks?
Liquidity in stocks means how easily a stock can be converted into cash. Highly liquid stocks are those that can be converted into cash easily and at the lowest cost, meaning at a price above the purchase price without a selling commission or with a low commission. For example, real estate is considered low-liquidity.
How are liquidity ratios linked to activity ratios?
Activity ratios (efficiency ratios) measure how efficiently a company uses its financial assets on the balance sheet and converts them into revenues. For example, how efficient is the company in managing inventory?
The higher the company’s activity ratios, the better its liquidity ratios, because it is better prepared to meet its short-term obligations through effective asset management and the speed with which it converts assets into cash.
What does a high liquidity ratio mean?
High liquidity ratios are a good indicator that the company can manage its assets and liabilities and repay lenders’ funds, and that it is far from liquidity crises, making it worthy of investors’ trust.
Which liquidity ratio is considered the strictest?
When talking about liquidity ratios, the cash ratio is considered the strictest because it relies only on cash and marketable securities. It is followed by the quick ratio, which excludes all current assets that are not cash or cash equivalents.
How can liquidity ratios be increased?
After learning about liquidity ratios and their importance, you are probably now thinking about how to increase liquidity ratios in your company. Below are the most successful 10 ways to improve liquidity ratios:
- Increasing inventory turnover, which refers to the speed of liquidating inventory and converting it into cash through faster sales.
- Shifting toward long-term financing.
- Paying urgent obligations regularly.
- Reducing liabilities and expenses such as rent and salaries.
- Converting unnecessary accounts into accounts with interest and high cash liquidity through sweep accounts.
- Accelerating the collection of customer receivables.
- Negotiating with creditors to defer the payment of some obligations, giving the company more time to generate liquidity.
- Developing effective marketing strategies that lead to increased sales and thus increased liquidity and cash flows.
- Identifying future cash needs contributes to planning to secure the required liquidity at the appropriate time.
- Securing credit sources that can be used when needed, providing additional liquidity, while paying attention not to increase debt ratios beyond the necessary limit to avoid financial risks of non-payment, such as bankruptcy, and others.
How can liquidity ratios be used effectively?
According to the accounting equation used to calculate liquidity ratios, the acceptable current ratio in most companies ranges from 1.5 to 2. In contrast, acceptable quick and cash ratios in most companies should not be below 1 to maintain financial stability and security.
What happens when ratios indicate that a company does not have sufficient liquidity?
When ratios indicate insufficient liquidity, financial problems or risks arise. Below are the consequences of losing liquidity in a company:
- Increased financial risks are associated with the inability to meet financial obligations.
- A decline in the company’s credit rating makes it difficult to obtain loans on favorable repayment or interest terms.
- Delays in paying suppliers, which negatively affect business relationships, lead to loss of trust with suppliers and lenders, and harm the company’s reputation in the market.
- Reduced liquidity may disrupt daily operations, reduce production, and weaken revenues.
- Declining growth opportunities due to the inability to expand into new investments because of insufficient liquidity.
Learn about the investment calculator to calculate the expected return on investments.
What is a good liquidity ratio?
A good liquidity ratio varies depending on the sector or industry, but in general, it is recommended that:
- The current ratio should be greater than 1.
- The quick ratio should be higher than 0.7.
- The cash ratio should be higher than 0.5.
Which financial ratios measure liquidity?
The financial ratios that measure liquidity are the current ratio, the quick ratio, and the cash ratio.
Which liquidity ratio is the most accurate?
The quick ratio is the most accurate liquidity ratio because it excludes inventory from current assets.
When is liquidity considered high?
Liquidity is considered high when the number of products sold increases, transactions are executed quickly, and buyers and sellers are readily available in the market.
What is the quick turnover ratio?
The quick turnover ratio is a financial measure that evaluates a company’s ability to repay short-term debts. A value of 1 or higher is considered a good indicator of the company’s ability to convert liquid assets into cash quickly.
What is the difference between liquidity and solvency?
The difference between liquidity and solvency lies in the speed of converting assets into cash. Liquidity focuses on meeting short-term obligations, while solvency focuses on meeting long-term commitments.
What is the difference between liquidity and costs?
Liquidity is a financial measure of the speed of converting assets into cash, while costs are the amounts spent on operating the company’s activities.
What is the statutory liquidity ratio?
The statutory liquidity ratio ranges between 20% and 40% and varies from one country to another. It represents the minimum percentage of deposits that a bank must retain as fixed assets.
What is the liquidity indicator?
The liquidity indicator is a measure used to evaluate cash flows and identify overbought and oversold signals.
How is the liquidity ratio calculated?
Calculate the liquidity ratio using the following formula:
Liquidity ratio = Current assets ÷ Current liabilities
What does a liquidity ratio of 1.5 mean?
A liquidity ratio of 1.5 indicates the company is in a healthy financial position and can cover short-term obligations, making it a favorable metric.
What does a liquidity ratio of 30% mean?
A liquidity ratio of 30% means that the company has financial value that covers only 30% of the debt value.
What is a very high liquidity ratio?
A very high liquidity ratio exceeds 3. This ratio may indicate one of two things: either the company has sufficient ability to cover its obligations, or it is not making optimal use of its assets.
What is the difference between profitability and liquidity?
The difference between profitability and liquidity is that profitability means the company generates profits through selling products or providing services, while liquidity is the company’s ability to convert assets into cash to repay debt.
How do we calculate the liquidity ratio?
Calculate the liquidity ratio using the following formula:
Liquidity ratio = Current assets / Current liabilities
What increases the liquidity ratio?
The liquidity ratio can be increased by improving capital management or reducing unproductive debt.
What does providing liquidity mean?
Providing liquidity means making the cash necessary to repay debt available in a short period of time.
What is excess liquidity?
Excess liquidity in banks means the presence of an amount of cash greater than market needs.
In conclusion, liquidity ratios are not merely numbers in financial reports but powerful indicators of a company’s actual performance and financial position.
Therefore, as a business owner or financial manager, always ensure you follow strategies to improve liquidity ratios and periodically assess the factors that affect them, to build a strong financial reputation based on efficient management of the company’s liquid assets.
















