Your Comprehensive Guide to Current Assets

Table of contents:
- What are current assets?
- What is the importance of current assets?
- Why are they called current assets?
- What are the types of current assets?
- What are the different examples of current assets?
- How are current assets calculated?
- What is the difference between current and non-current assets?
- What is the difference between current assets and current liabilities?
- Frequently Asked Questions about Current Assets
- Current Assets in Daftra
To assess an organization's liquidity, look at its current assets. From this perspective, current assets are those that can be converted into cash. Any short-term property that lasts less than a year is considered a current asset and can be used by the organization.
It is well known that current assets appear on the entity’s balance sheet, so one can assess the organization’s liquidity by examining its financial position and understanding its classifications and types. They also reflect the organization's financial capability, whether it can meet its obligations.
In this article, we will examine the definition of current assets, their types, how to calculate them, the differences between current and fixed assets, and related questions.
What are current assets?
They are personal property of any organization, but they are properties that do not last more than a year, that is, short-term. These assets are easily convertible to cash. Current assets are presented in the financial position by liquidity, with the most liquid asset listed first. They are considered a fundamental component of the organization’s working capital.
Current assets indicate the organization's ability to meet current liabilities and other short-term obligations. Investors always look at an organization’s financial position, including current and fixed assets, as this provides them with a sense of security.
Read also: Definition of the term Current Assets.
What is the importance of current assets?
The importance of short-term assets for companies can be understood through their impact on financial operations, their role in stabilizing the company’s financial position, and their ability to convert any asset into a financial source within a specific period. The following points highlight the importance of current assets:
- In the event of a crisis within the organization, it is easier to manage current assets because they can be converted into cash quickly.
- They indicate an organization's liquidity by summing its current assets.
- Understanding the organization's financial position helps make future decisions.
- They determine the potential risks to the organization’s position, which helps assess the feasibility of the investment.
- The total current assets indicate whether the organization can meet its future obligations.
Therefore, current assets are indispensable to any organization, and company owners and accountants seek to maximize their value in the financial statement, which requires professional financial management.
Why are they called current assets?
Current assets are also referred to as circulating or liquid assets and are sometimes called short-term assets. This is because they refer to assets that are actively traded in financial markets, intending to generate financial returns as quickly as possible.
What are the types of current assets?
Companies' current assets come in several types and can be converted into cash within a specific period. This period varies by the type of current asset being converted into cash. The following are the different types of current assets:
1- Cash and cash equivalents
Every organization owns liquid funds, but what is considered cash and classified as a current asset?
It can be: bank current accounts, treasury bills, savings accounts, and money transfers.
All these items are cash equivalents, meaning they can be readily converted into cash.
2- Short-term investments
These are temporary investments that can be liquidated within one year only. Examples of these securities include: Stocks, Government bonds, and Certificates of deposit.
Use the investment calculator to calculate the profit from the investment based on the amount invested.
3- Accounts receivable
These are the amounts owed by customers for goods and services delivered. They represent the cash due to the organization from its customers.
4- Inventory
Inventory is considered a current (circulating) asset of the organization and can be classified as:
- Raw materials
- Work-in-progress
- Finished products
Inventory is one of the most important current assets, especially when there are significant sales, as it can be easily converted into cash.
5- Prepaid expenses
The organization pays expenses in advance to obtain goods or services. This is the only asset not measured by liquidity; it represents payments made to avoid future cash outflows.
Examples include Prepaid taxes and insurance premiums.
After clarifying the different types of current assets, we note that most are cash, inventory, short-term investments, and prepaid expenses. Examples of these include the following.
What are the different examples of current assets?
Continuing from the point about the different types of current assets, we can present various examples of current assets, whether they are assets currently owned by the company or assets located elsewhere. The following are some of these current assets:
- Postal and bank transfers
- Money market accounts
- Stocks and bonds
- Recurring product withdrawals
- Insurance payments
- Cash
- Unpaid receipts (Accounts receivable)
- Investment funds
- Semi-annual fees
- Prepaid rent
- Marketable securities
Other types of current assets vary by company type and activity, but the above account for the most commonly recognized short-term assets.
How are current assets calculated?
To calculate current assets, we follow several steps to determine the total current assets within the company. Calculating current assets helps in evaluating the company’s financial position. The following will provide a detailed explanation of each step to answer the question: “How do I calculate current assets?”
1- Cash calculation
In this step of calculating short-term assets, cash on hand is added together with all petty cash and current accounts.
For example, if the organization has cash on hand of $50,000, a current account balance of $100,000, and petty cash of $40,000, the cash under current assets can be calculated as follows:
50,000 + 100,000 + 40,000 = $190,000 in the cash account.
Using the available solutions in the Daftra system, you can determine the company’s cash on hand through the asset management program. Additionally, petty cash can be identified through sales reports in Daftra.
2- Total short-term investments
All short-term investments are added together. For example, if the organization owns $30,000 in stocks and $20,000 in certificates of deposit, the total short-term investments account is $50,000.
3- Total accounts receivable
All amounts owed to the organization by customers are added together, whether collected or not.
You can track the company’s customer receivables in the Customer Management program within the Daftra system and monitor all payments due from each client.
4- Total inventory calculation
Inventory at the end of the year can be calculated using the following formula:
Inventory at the beginning of the year + Net purchases – Cost of goods sold
Through the Inventory Management and Stocktaking programs in Daftra, you can find the value of inventory at the beginning of the year. Based on this, you can calculate the total inventory. Net purchases can also be determined through the Purchasing Management program in Daftra, which tracks purchases for a specific period.
For example:
If the beginning inventory is $100,000, net purchases for the year are $150,000, and the cost of goods sold during this period is $75,000,
Then the ending inventory value is:
100,000 + (150,000 – 75,000) = $175,000.
Finally, to calculate total current assets, the following formula should be used:
Cash + Cash equivalents + Total short-term investments + Accounts receivable + Inventory + All prepaid expenses + Total other assets
What is the difference between current and non-current assets?
The difference between current and non-current assets is as follows: current assets are those that can be converted into cash within a short period and support short-term operational activities, whereas non-current assets are those that can be converted into cash over a long period and support long-term operational activities.
- Current assets: These are assets that can be easily converted into cash and do not last more than one year (short-term).
- Non-current (fixed) assets: These are assets used by the organization to generate income and for production processes. They cannot be easily converted into cash and last for many years (long-term).
- Examples of current assets: Cash, Inventory, Accounts receivable, Securities, Certificates of deposit, Prepaid insurance.
- Examples of non-current (fixed) assets: Land, Buildings, Machinery and equipment, and furniture.
What is the difference between current assets and current liabilities?
Current assets are the organization’s properties that can be easily converted into cash. They increase working capital and indicate the organization’s liquidity. On the other hand, current liabilities are obligations the company must settle within a short period. They reduce working capital and pose a risk to the organization’s liquidity.
| Comparison Point | Current Assets | Current Liabilities |
| Definition | Organization’s properties that can be easily converted into cash and are short-term. | Obligations the organization must settle within a short period. They are settled using current assets. |
| Effect on working capital | Increase working capital | Decrease working capital |
| Placement in the financial position | Listed under assets | Listed under liabilities |
| Relation to organizational liquidity | Known to indicate the organization’s liquidity; the higher they are, the higher the liquidity | Pose a threat to the organization’s liquidity if they increase |
| Examples | Marketable securities – Bank current accounts – Inventory | Bank overdrafts – Promissory notes – Accounts payable |
Frequently Asked Questions about Current Assets
Are loans considered current assets?
There are two cases to answer this question:
- If the loan is granted to the organization, it is a debt and a liability for the organization.
- If the organization grants a loan to another party, it is a loan receivable.
However, if the loan is short-term and its duration does not exceed one year, it is classified as a current liability in the first case and as a current asset in the second.
What is the relationship between working capital and current assets?
There is a well-known formula that illustrates the relationship between working capital and current assets:
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
Therefore, any organization that wants to determine its working capital first calculates total current assets and then subtracts total current liabilities.
Is inventory considered a current asset?
Inventory is classified as a current asset if the organization intends to sell it within the year. Inventory is a primary source of revenue and is considered highly liquid compared to non-current assets.
What are net current assets?
Net current assets are the remaining amount of total current assets after paying off debts (current liabilities), also known as working capital.
Their value can be positive or negative and serves as an indicator of the business’s financial health.
- If current assets exceed current liabilities, this means the organization can pay its debts.
- If current liabilities exceed current assets, this indicates the organization is unable to meet its debt obligations.
What does the term “Zero Working Capital” mean?
This term means that working capital equals zero, i.e.:
Current Assets – Current Liabilities = 0
or Current Assets = Current Liabilities
Is a bank considered a current asset?
A bank, as an institution, is not considered a current asset because this type of asset includes financial instruments that can be bought or sold in the market to earn returns quickly, not organizations or institutions. However, bank-issued instruments such as stocks, bonds, and securities can be considered current assets.
Are debtors considered current assets?
Yes, debtors are considered current assets because they represent individuals or companies that owe the organization money as a result of selling goods or providing services on credit. These amounts are expected to be collected within the organization’s normal operating cycle, typically within one year.
Are promissory notes considered current assets?
Yes, promissory notes are considered current assets. They are documents representing financial claims that can be collected and converted into cash during the company’s normal operating cycle.
Is merchandise considered a current asset?
Merchandise is classified as a current asset because it consists of goods and products held by the company for resale. It is expected to be converted into cash within the company’s operating cycle, typically within one year.
What is the ideal current asset ratio?
A good current asset ratio is 2:1, indicating that the company has twice as many current assets as current liabilities. The ratio can be calculated using the following formula:
Current Assets / Current Liabilities = Ratio
You can use a percentage calculator to find the ratio between two numbers or determine the ratio from any given amounts.
Is capital considered a current asset?
No, capital is not a current asset. Capital refers to the funds the company uses to operate the business and finance investment activities, whereas current assets represent liquidity that can be used to manage daily operations and cover short-term obligations.
How are current assets arranged by liquidity?
Current assets are arranged from most liquid to least liquid as follows:
- Cash in hand and bank current accounts
- Short-term securities such as stocks and bonds
- Inventory (merchandise)
- Accounts receivable
What are the steps for taking inventory of current assets?
- Determine the period used to count current assets.
- Form a team responsible for the inventory process.
- Collect all current asset items available during the specified inventory period.
- Decide the method for valuing assets, including inventory and accounts receivable. Methods may include the cost method, the market value method, the cash flow method, or the financial ratios method.
- Use an integrated cloud accounting system, such as Daftra, to accurately gather current asset data from financial records, invoices, and other sources.
- Conduct the physical inventory of current assets.
- Document inventory results and record any discrepancies between actual assets and accounting records.
- Analyze discrepancies and verify their causes.
- Update accounting records based on the inventory results.
- Prepare an inventory report, including recommendations to help efficiently manage current assets.
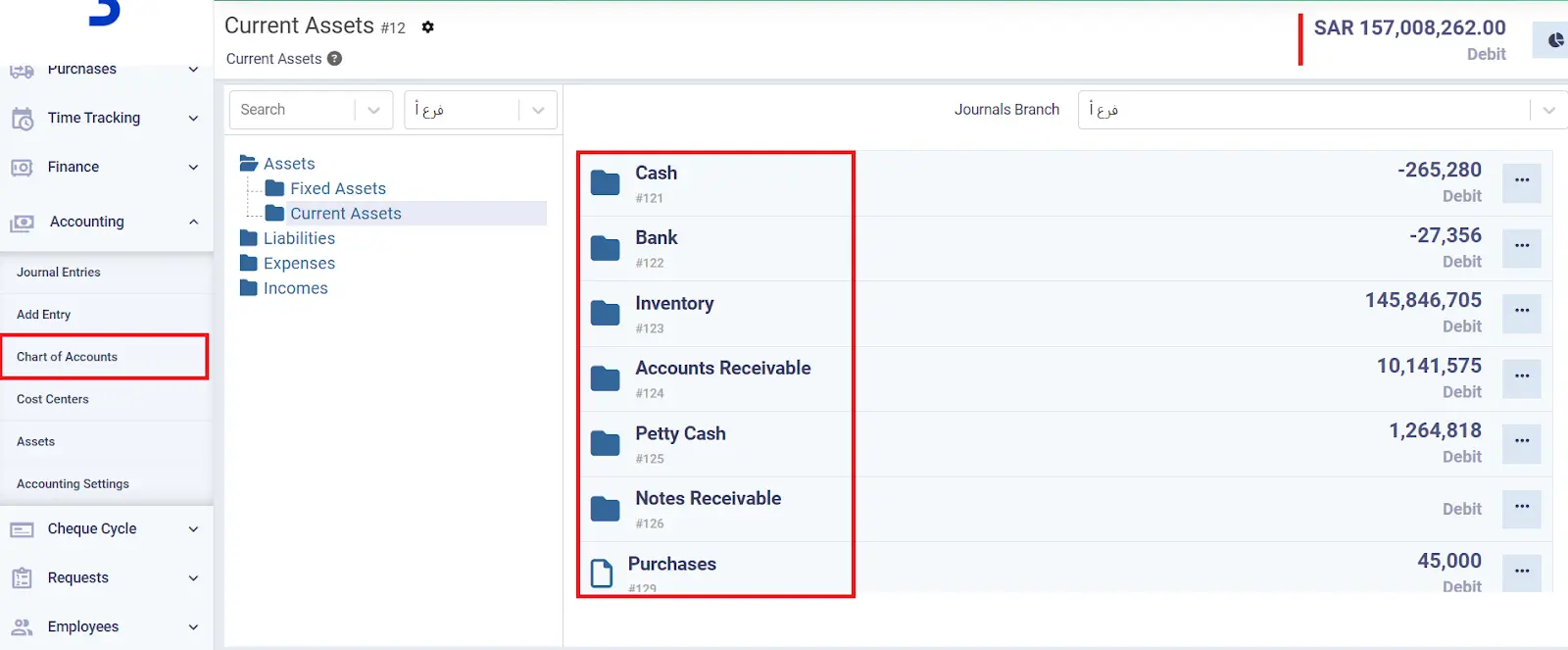
Current Assets in Daftra
In the Chart of Accounts available in the Daftra accounting software, under the Assets section, there is a Current Assets category. This category is subdivided into types, each representing one of the classifications of current assets, as follows:
- Cash on Hand
- Bank
- Inventory
- Debtors
- Notes Receivable
- Employee Custodies
- Purchases (Returns)
- Currency Exchange
- Notes Receivable
- Amounts Under Collection
- Advances
In addition, it is possible to add new classifications for current assets. There is also a comprehensive asset management program. By clicking on any of these items, you can view the accounting entries and operations related to these assets, as well as the available cash. This allows you to know their total value in order to assess your financial position and estimate the level of liquidity available in your account at the present time.